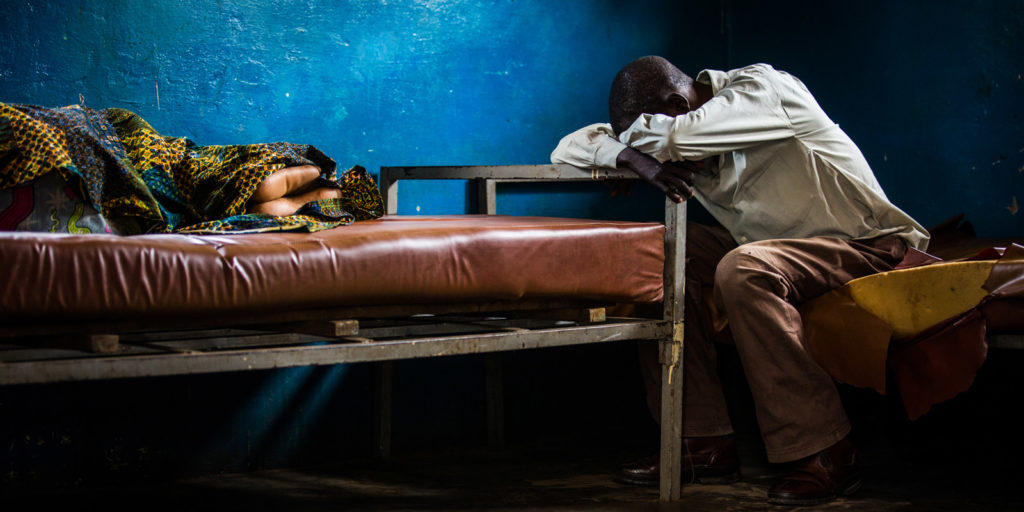
WILLS POINT, TX – Gospel for Asia (GFA) issues an extensive Special Report on the deadly diseases brought by the mosquito and the storied impact of faith-based organizations on world health, fighting for the Kingdom to “come on earth as it is in heaven.”
It takes only one mosquito, buzzing around with ill intent, dive-bombing in the middle of the night, hovering ominously around a would-be sleeper’s ear, to cause alert wakefulness and ruin the REM-phase of deep slumber. Five or six mosquitoes, all in disharmonic buzzing in one room, demand that the sleepy occupants get up and destroy the pesky insects, no matter how many bug guts get left on the walls.
Interestingly, research about the ubiquitous presence of the mosquito led me to a startling discovery about the Gospel’s mostly unknown and stunning impact on the development of the World Health Organization’s (WHO) eight Millennium Development Goals. This is an article about that impact. Let me start at the beginning.
My son Jeremy, post-college and conveniently fluent in Spanish, was helping me with a writing project in Mexico thanks to some excess flight mileage points. Jeremy, at that time, was a counselor for World Relief, an international organization that assists churches to sponsor refugees. He had become proficient in dealing with immigration issues and consequently was open to being bribed by his mother to spend five work-and-play days on the Mexican Riviera.
One night, we returned to our room unaware the maid had neglected to close the screenless windows after cleaning. Finally resigned to the reality that hiding under the sheets was a futile deterrent against bloodthirsty pests, we turned on the lights and did battle royal, swinging towels and rolled-up manuscripts, until we were certain that not a single mosquito had survived the slaughter.
And yes, there were bug guts all over the walls.
I remember falling to sleep that night, deeply satisfied with our search-and-destroy mission, and suddenly catching myself thinking: What if this were a malaria-ridden country? It would only take one mosquito, the female anopheles, to transmit one of the parasites on the spectrum belonging to the genus Plasmodium. It only takes one mosquito bite in a person lacking immunity to bloom into rampant malaria some 10–15 days later.
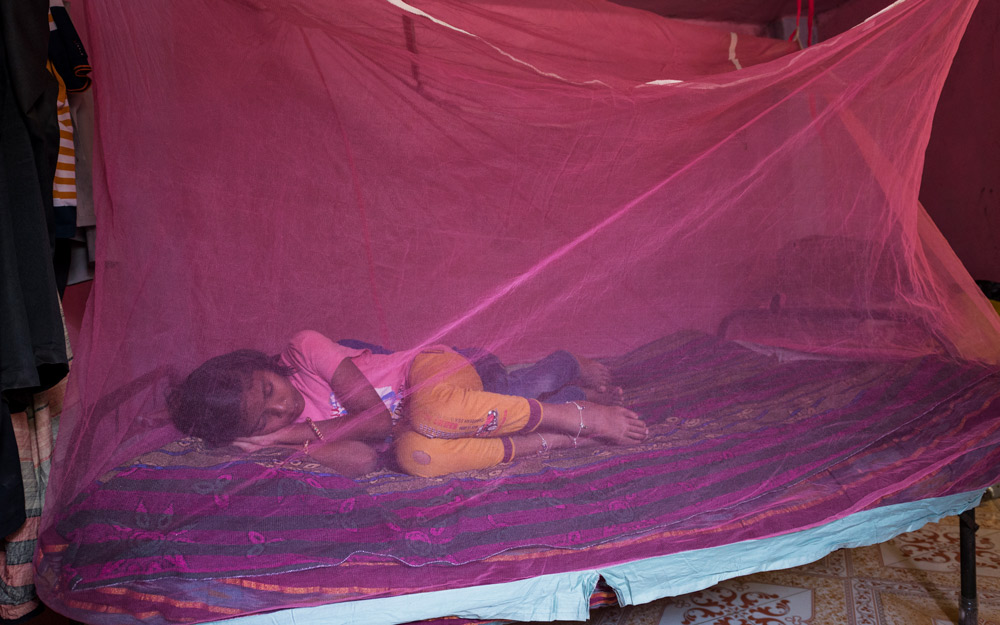

Mosquitoes Nets Versus Malaria
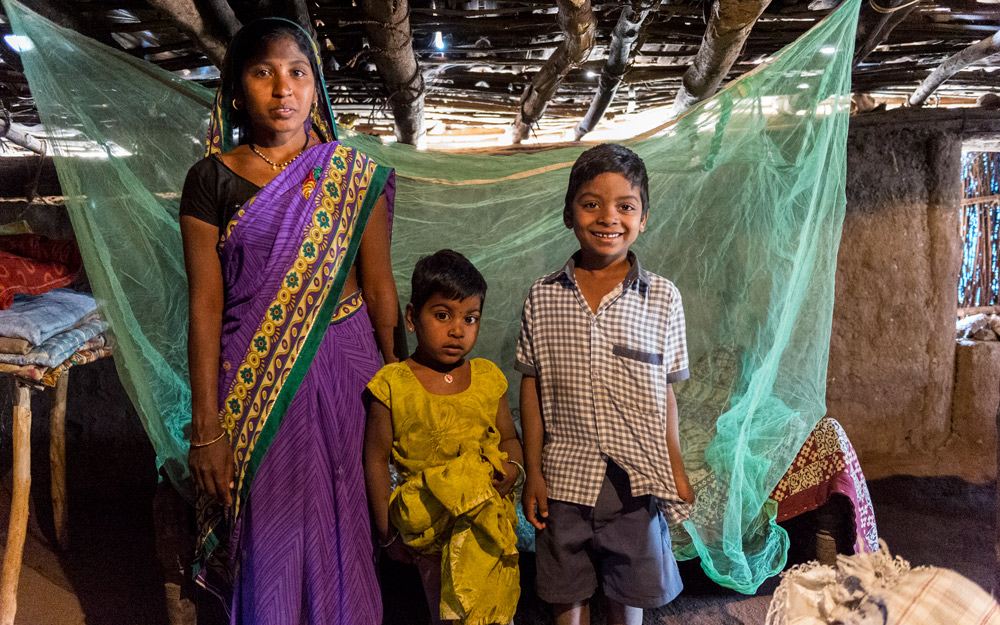
It may seem strange in countries or communities that maintain sophisticated mosquito abatement programs to learn that mosquito nets across the world are one of the most important means of saving lives.

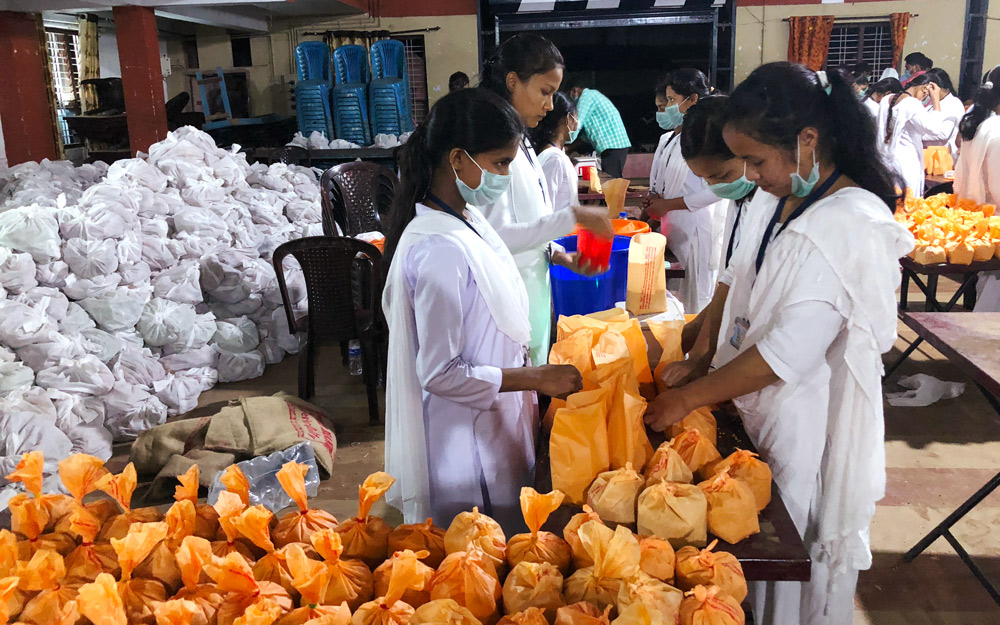
Gospel for Asia (GFA) tells the story of Pastor Ojayit walking through villages and inquiring of residents as to whether they had been afflicted by malaria and if they needed mosquito nets. (These, for those who are unaware, are hung over beds, sleeping cots or hammocks at night.) The pastor was deeply moved by the numerous folk who had suffered with the mosquito-borne illness. One man named Madin, along with his family, had been ill with malaria and brain malaria on several occasions. Extreme poverty kept the family from affording medication or prevention treatments to combat the disease or the airborne insects that carried the disease.
Pastor Ojayit added Madin’s name to the list of recipients for the next Gospel for Asia (GFA)-supported Christmas gift distribution so he could receive a mosquito net. That simple gift meant, for the first time, Madin and his family began to thrive. The children could attend school; they all could gain back health. The gift of a mosquito net also demonstrated the practical application of God’s love and concern for the people of the world.
A mosquito net can be the difference between life and death—but the fight with malaria is far from over.
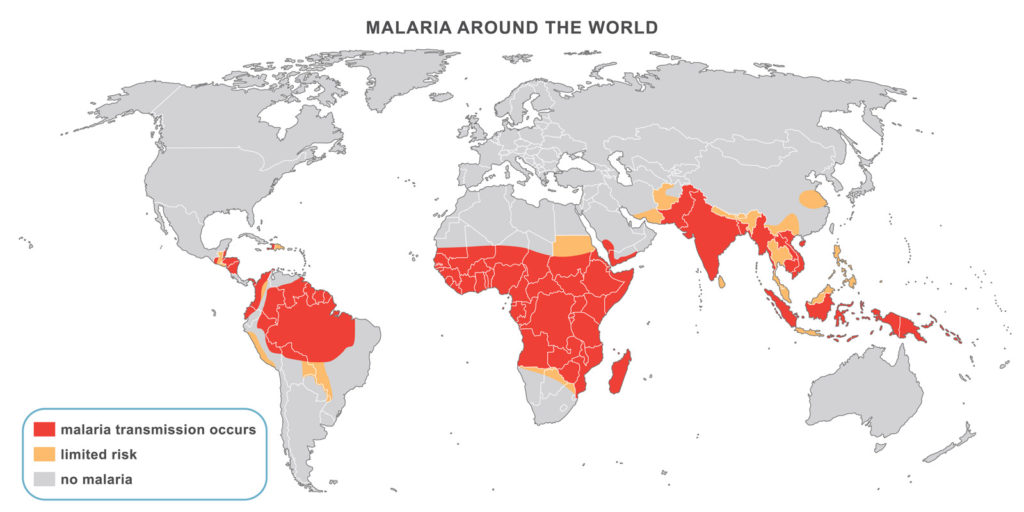
The 2018 World Malaria Report indicated that in 2017, after an unprecedented period of early success stimulated by the World Health Organization’s campaign to bring malaria under global control, progress in fighting the disease has stalled. There were an estimated 219 million cases and 435,000 related deaths in 2017. This was up from 217 million cases in 2016. Evaluations as to the possible cause of this slide include a decrease of billions of donor dollars due to other disastrous disease episodes worldwide.
The report also added that 11 countries bear 70 percent of the burden of this particular global disease: Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ghana, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Uganda, Tanzania and India, most of them in tropical or subtropical areas of the world, most often where there are impoverished populations.
Millennium Development Goals & Millennium Sustainable Development Goals
Despite this setback in malaria eradication, health indicators from around the world show that a handful of the eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), introduced by the World Health Organization and announced in September 2000, are meeting or exceeding fulfillment expectations. The eight Millennium Development Goals are:

The WHO Declaration notes that the “MDGs are inter-dependent; all the MDGs influence health, and health influences all the MDGs. For example, better health enables children to learn and adults to learn. Gender equality is essential to the achievement of better health. Reducing poverty, hunger and environmental degradation positively influences, but also depends on, better health.”
So how is the world doing?
Despite the United Nations declaring this international effort “the most successful anti-poverty movement in history,” success is also a much more daunting task than the optimistic planners imagined. Since 2015, the MDGs morphed into the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals with 17 points and a more realistic target accomplishment date of 2030.
And why is that? Well, it’s just plain difficult to create a peaceable, equitable, egalitarian world system that dignifies the life of every human on the planet. Huge progress has been made in four out of the eight MDGs; extreme poverty levels, for instance, have been almost halved globally. Gender disparity goals in education were nearly met, new HIV infection levels were reduced by 40 percent and the world did reach the goal on access to safe drinking water. However, unprecedented weather crises, rising conflict causing unanticipated migration patterns, the lack of high-level technology in many places for data gathering and more defeated the optimistic intents of the planner.
With all this as a background, now let’s focus on Millennium Development Goal #8, “to develop a global partnership for development.”
How have faith-based organizations impacted health initiatives in the modern era? The backstory to these simple seven words in goal #8 contains an excellent, if not elegant, example of the interaction of faith-based theology and compassionate intent on the policy-making behind the World Health Organization’s vital Declaration, which many world-watchers consider a watershed in the history of international development. This is a story that needs to be told and understood because it provides a map to effectuate more positive results to a world in crisis.
Faith-Based Organizations as Seen Through the Bite of the Mosquito
Let’s look at that mosquito again, the anopheles that carries some form of the genus Plasmodium, which is the genesis of several strains of potentially deadly malaria parasites. In addition to malaria, the bite of various mosquitoes can also transmit dengue and yellow fever as well as the Zika, West Nile and African Sleeping Sickness viruses. The long battle against the lone mosquito multiplied by millions of its kind presents a simulacrum through which an enormous topic—modern medicine outreaches as influenced by faith—can be viewed.
600,000
mosquito nets distributed in 2016 by GFA-supported workers
One of the specific health ministries Gospel for Asia (GFA) initiated in 2016 was to participate in World Mosquito Day, observed every August 20 to raise awareness about the deadly impact of mosquitoes. This global initiative encourages local governments to help control malaria outbreaks, and it also raises funds from large donor organizations and national governments to underwrite worldwide eradication efforts. Discovering and applying means of mosquito control in overpopulated areas of the world is essential, but the task is so large and the enemy so canny that planners have discovered they must rely on a combination of efforts that activate local communities and the leaders in those communities, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), faith-based organizations (FBOs) and faith-based development organizations (FBDOs).
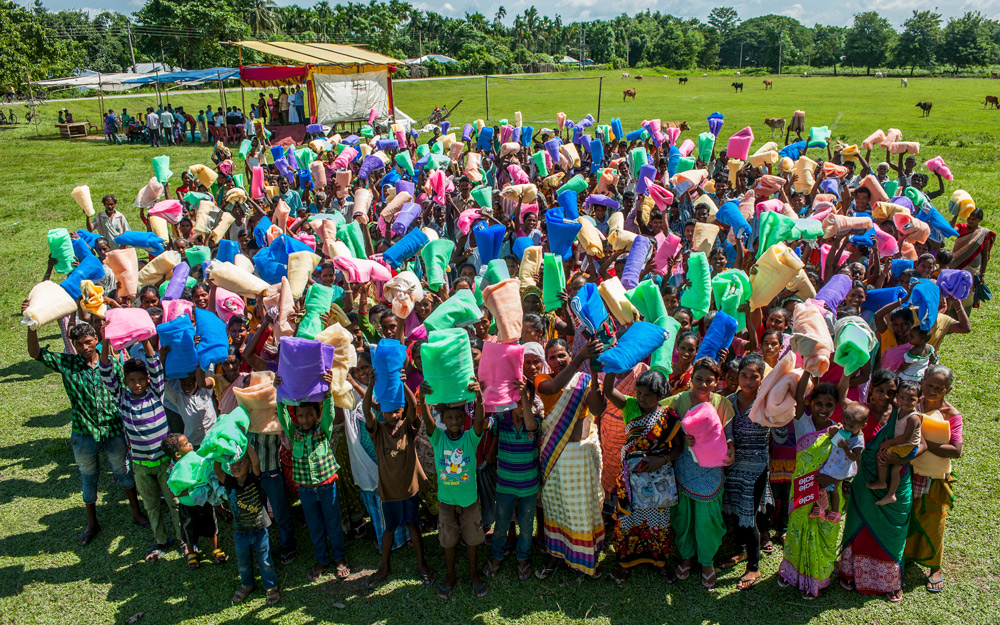
In 2016, workers collaborating with Gospel for Asia (GFA) distributed some 600,000 mosquito nets, many of which were given to people living in districts where there are high malaria risks and high poverty levels. Due to poverty, these folks were unable to procure the simplest of means to prevent mosquito-borne diseases. In addition to the nets, which were given away without charge, Gospel for Asia (GFA) conducted disease-awareness training in order to heighten understanding about preventive measures.
This effort was compatible with the movement back to a primary health care emphasis as delineated in the 1978 Alma-Ata Declaration encouraged by the World Health Organization, which proclaimed the principles of what was meant by the concept of primary health care and the overreaching need for it. While a few populations in developing countries have access to tertiary health care—hospitals and clinics and professionals trained in medical schools, drugs and diagnostic equipment—the vast majority of the rest of the populace can access extremely limited or next-to-no available health care. In the majority of rural areas, for instance, there are no clinics, no hospitals, no medical professionals and no treatment protocols. (This medical desert is also becoming a problem in the United States; as rural populations shrink, hospitals and clinics cannot afford to stay open.)
The Alma-Ata conference recommended a redirection of approaches to what is termed primary health care. Charles Elliott, an Anglican priest and development economist, summarized the suggested changes as follows:
- An increasing reliance on paraprofessionals (often referred to as community health workers) as frontline care givers;
- The addition of preventive medicine to curative approaches;
- A noticeable shift from vertical, disease-specific global health initiatives to integrated, intersectoral programs;
- A willingness to challenge the dominant cost-effectiveness of analysis, particularly as it was used to justify a disproportionate distribution of health care resources for urban areas; and
- A heightened sensitivity to the practices of traditional healing as complementary rather than contradictory to the dominant Western medical model.
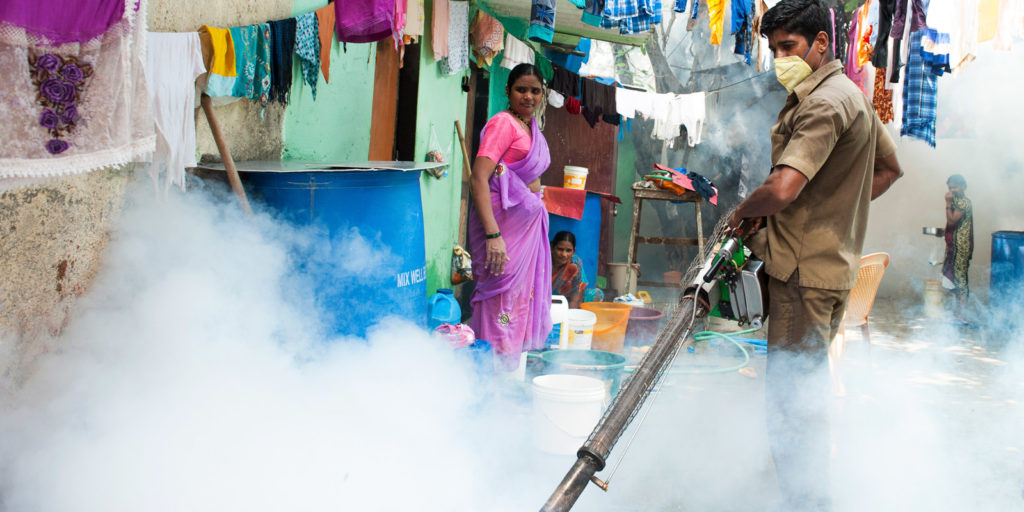

India’s Progress in Combating Malaria
In 2015, the World Health Organization set a goal of a 40 percent reduction in malaria cases and deaths by 2020 and estimated that by that deadline, malaria could be eradicated in 11 countries. The first data reports were extremely encouraging, but attrition began to set in, due to what experts feel is a lag in the billions of donor funds needed to combat the disease. The 2018 World Malaria Report health data now indicate a slowing in the elimination of the disease and even growth in disease incidents and deaths. This slide is disheartening to world health officials, particularly since early reports gave evidence of real impact against morbidity.
India, however, according to the 2018 report, is making substantial progress: “Of the 11 highest burden countries worldwide, India is the only one to have recorded a substantial decline in malaria cases in 2017.”
The report goes on to state that the country, which accounted for some 4 percent of global malaria cases, registered a 24 percent reduction in cases over 2016. The country’s emphasis has been to focus on the highly malarious state of Odisha. The successful efforts were attributed to a renewed government emphasis with increased domestic funding, the network of Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs)—an intended 900,000 women assigned to every village with a population of at least 1,000—and strengthened technological tracking, which allowed for a focus on the right mix of control measures. The aim of India’s National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme is the eradication of malaria.
Remember the ever-present mosquito? Studies conducted by WHO released the findings of a major five-year evaluation reporting that people who slept under long-lasting insecticidal nets had significantly lower rates of malaria infection than those who did not use a net.
In coordination with this national effort, GFA-supported workers distributed nets to villagers, in student hostels, among workers in the tea-growing district of Assam and many other areas while at the same time leading disease-awareness programs to tea-garden employees.

Imagine a dusty village filled with women wearing vibrant-colored clothing. Little children dance around or stand intrigued, their huge brown eyes open. Nets are placed into outstretched hands. Women smile; gifts are always appreciated. Men listen carefully to the reasons why bed nets are essential and why it is necessary to spray the home and rooms. People bow their heads; they raise pressed hands to their faces. “Namaste,” they say giving thanks.
Envision a room at night with six to eight buzzing, dive-bombing mosquitoes and give thanks that there are organizations around the world that pass out the free gift of bed nets that not only keep humans from being stung but also prevent them from becoming wretchedly ill.
Historical Cooperation
The possibility of eradicating malaria rests in the efforts of Dr. Ronald Ross, born in Almora, India, in 1857 to Sir C.C.G. Ross, a Scotsman who became a general in the Indian Army. Reluctant to go into medicine, the son nevertheless bowed to his father’s wishes to enter the Indian Medical Service.
At first, Ross was unconvinced that mosquitoes could possibly be carriers of malaria bacteria, yet his painstaking, mostly underfunded laboratory discoveries eventually convinced him that the hypothesis of a mentor, Patrick Manson, an early proponent of the mosquito-borne malaria theory, was correct. (Manson is also considered by many to be the father of tropical medicine.) Another contemporary, the French Army doctor Alphonse Laveran, while serving at a military hospital in Algeria, had observed and identified the presence of parasitic protozoans as causative agents of infectious diseases such as malaria and African Sleeping Sickness.

On August 20, 1897, in Secunderabad, Ross made his landmark discovery: the presence of the malaria parasite in humans carried by the bite of infected mosquitoes. (For obvious reasons, Ross was also the founder of World Mosquito Day.) Disease can’t be combated unless its source is identified, nor can it be optimally controlled. Certainly, without this knowledge, it can’t be eradicated. In 1902, Ronald Ross was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
Here again, through the bite of the mosquito, we see the collaborative effort that undergirds progress. Three doctors intrigued with conquering the morbidity of disease take painstaking efforts to prove their theories, and each one builds on the discoveries of the other, with eventual dramatic results.

Change Involves Everyone
Progress is not possible without collaborative work. Statisticians, medical teams and universities, as well as local village training centers, governments of developing countries and local leadership in towns and cities must all work together. The job requires donations from wealthy donor nations as well as from national local budgets. We need the skills of technological gurus, engineers and the extraordinary capabilities of highly trained health care professionals and sociologists. In addition, we also need the involvement of those who care about the soul of humans and who have insisted, because their lives are driven and informed by a compassionate theology, that every human is made in the image of God.
Gospel for Asia (GFA), through its mosquito net distribution—and its many other ministries—stands central in the contemporary initiatives of health-based, community-centered, preventive health care.
These are some of the strategic players who must all be involved, and stay involved, if the MDGs, now the Millennium Sustainable Development Goals, are to be reached.
This model of interactivity, whether present-day players realize it or not, intriguingly stems from a decades-old initiative stimulated by the World Council of Churches (WCC) in the last century, based in a carefully crafted theological understanding by the Christian Medical Commission (CMC), which concurrently and cooperatively developed the meaning of health that simultaneously contributed to the WHO’s significant 1978 Declaration of Alma-Ata. This resulted in a focus on primary care as a more just and egalitarian way to distribute resources in order to treat a larger proportion of the world’s population.

This forgotten story needs to be resurrected because it demonstrates the power of intentional intersectoral cooperation between secular and religious health outreaches. It also exemplifies a more holistic redefinition of the meaning of health that has the potential to positively impact disease-ridden environments in the many populations that are generally minimally treated or completely untreated in developing countries. In a day when Western technologically centered medicine, driven by what some in health communities are starting to call the “industrial medical complex,” is beginning to wane in its understanding of the meaning of superior patient-centered care, this model needs to be adapted to what we think of as the more sophisticated treatment approaches in health care.
Our Friends, the Critics (Because Their Criticism Makes Us Think)
Let’s first take a quick look at what critics of faith-based medical outreaches have to say. Instead of delving into the academic literature, which though informative often provides a tedious plod through footnotes and specialized terminology, let’s look at the growing field of “opinion” journalism.

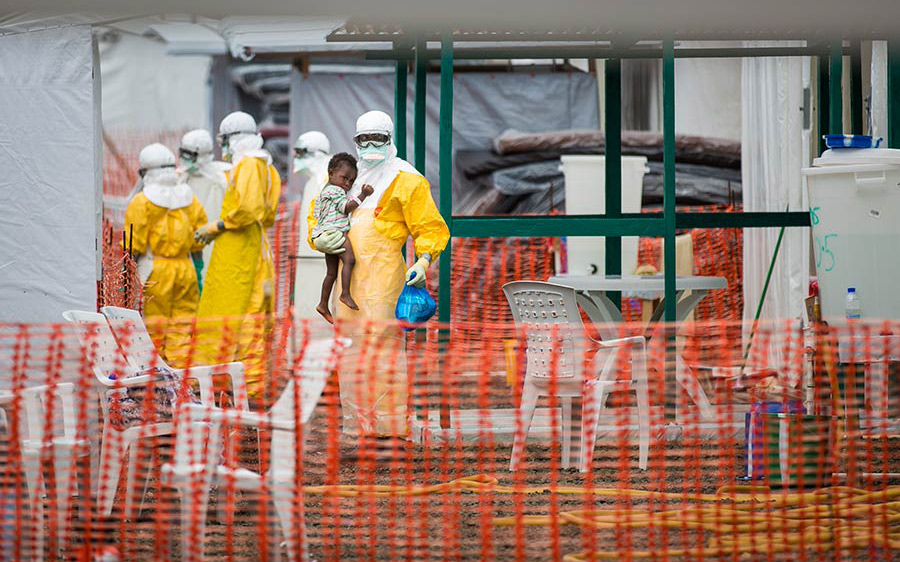
After the 2014 Ebola outbreak in Liberia, Africa, an article appeared in Slate Magazine by Brian Palmer, a journalist who covers science and medicine for the online magazine. This periodical represents an admittedly liberal perspective, and that bias, though the author attempts to play fair, is shown even in the headline to his report: In Medicine We Trust: Should we worry that so many of the doctors treating Ebola in Africa are missionaries?” Great lead line; it certainly caught the attention of my friends and colleagues who work in medical missions.
Palmer summarizes his basic critique in this paragraph: “There are a few legitimate reasons to question the missionary model, starting with the troubling lack of data in missionary medicine. When I write about medical issues, I usually spend hours scouring PubMed, a research publications database from the National Institutes of Health, for data to support my story. You can’t do that with missionary work, because few organizations produce the kind of rigorous, peer-reviewed data that is required in the age of evidence-based medicine.”
Although PubMed is a worthy venue for medical specialists as well as the generalist writing in the field—with some 5.3 million archived articles on medical and health-related topics—it alone may be a truncated resource for the kind of information that could have more richly framed this article. Interviews with at least a few boots-on-the-ground, living faith-based medical professionals who have given their lives to wrestling with the health care needs in countries far afield from Western medical resources, might also have been a better means of achieving a professional journalistic approach. In addition, there is a whole body of evidence-based research that a superficial treatment such as this did not access.

Sharon Bieber of Medical Ambassadors International responds to the Slate article out of a lifetime of framing health care systems with her husband, Dr. Bill Bieber, in mostly underdeveloped nations in the world. It is important to note the Canadian government awarded these “medical missionary types” the Meritorious Service Medal—an award established by Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II to be given to extraordinary people who make Canada proud—for their work of establishing the Calgary Urban Project Society. The Calgary Urban Project Society became the model across all Canada for helping those most in need (many of them homeless) by providing health care, education and housing—all this long before the concept of holistic treatment or an integrated approach engaging mind, body and spirit was part of the common literacy of health professionals. This, to be noted, was accomplished by the Biebers while on an extended furlough while their children finished high school—an interregnum before the two headed back to the South China Seas to fulfill their lifetime calling of working with national governments to establish primary health care systems along with improving tertiary systems in the countries where they landed.
Bieber writes, “Author Brian Palmer even queries the reliability of the mission doctors, who work in adverse and under-resourced conditions. The lack of trust seems to be justifiable, he infers, because they rarely publish their accomplishments in the ivory towers of academia! When they explain to patients they are motivated by the love of Jesus rather than financial gain, somehow that is ‘proselytizing.’ Would it be nobler, I wonder, if doctors were to tell them that the danger pay was good or that they desire adventure or fame? These are unproductive and unfounded arguments by critics who clearly have their own axes to grind, and at a time when the world crisis calls for everyone to roll up their sleeves and get to work in solving the problems facing us all.
“Surely the relief and development organizations that are out there in the world can come to the same conclusion on this one thing—everybody is needed in order to fight diseases such as Ebola, HIV/AIDS or tuberculosis; every agency has strengths that will add to the synergy of the whole. Whether faith-based, local and national government or secular NGO, all have been trained in similar techniques and scientific method. Collaboration is what is needed in order for groups that are stronger to support those that are less resourced to achieve a common goal.”
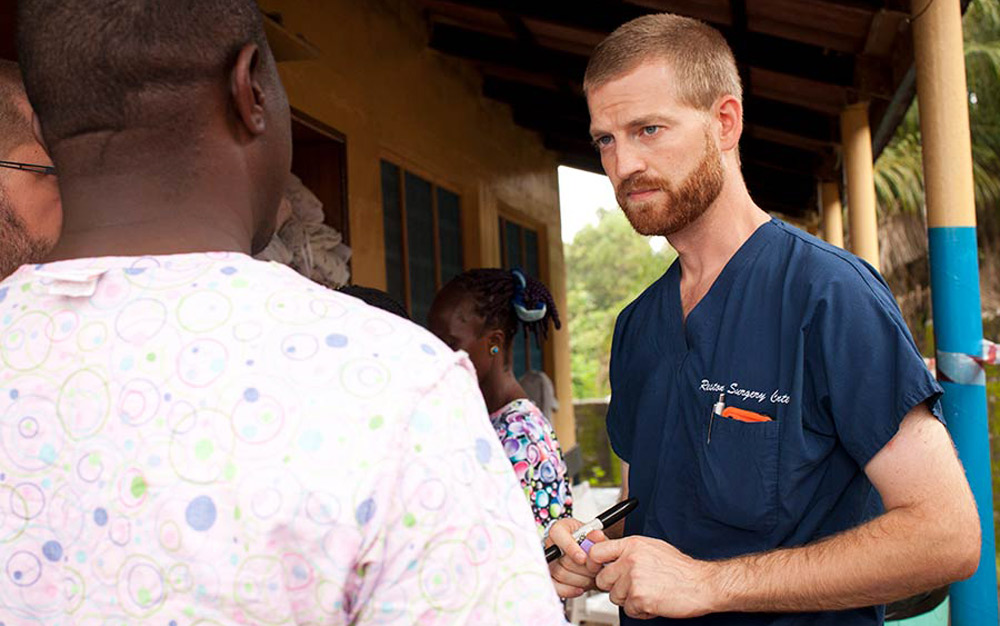
To be fair, the Slate journalist admits to being conflicted. After listing the flaws of medical mission approaches, Palmer writes, “And yet, truth be told, these valid critiques don’t fully explain my discomfort with missionary medicine. If we had thousands of secular doctors doing exactly the same work, I would probably excuse most of these flaws. ‘They’re doing work no one else will,’ I would say. ‘You can’t expect perfection.’ ”
At least he admits to bias. Knowing my share of medical missionaries, many of whom I consider truly heroic and who are radicalizing the health care systems of the countries in which they serve for the undeniable betterment of those societies, Palmer’s approach seems a tad unprofessional as far as journalism goes. He concludes, “As an atheist, I try to make choices based on evidence and reason. So until we’re finally ready to invest heavily in secular medicine for Africa, I suggest we stand aside and let God do His work.”
A deeper search in PubMed, driven admittedly by my own bias, led me to the excellent data-informed article utilizing research on the topic from both the scientific, theological and academic sectors by Jeff Levin, titled “Partnerships between the faith-based and medical sectors: Implications for preventive medicine and public health.”
Levin concludes with a quotation that complements his conclusion: “Former U.S. Surgeon General David Satcher, a widely revered public health leader, has made this very point: ‘Through partnership with faith organizations and the use of health promotion and disease-prevention sciences, we can form a mighty alliance to build strong, healthy, and productive communities.’ There is historical precedent for such an alliance, and informed by science and scholarship, it is in our best interest for this to continue and to flourish.”

How many of us in the faith-based sector have wrestled with the theological meaning of health? What is the history of the impact of faith (particularly Christian faith because that is the bias from which I write) on the ongoing movement of medicine in these modern centuries? Why does it matter?
I recently experienced a small snapshot of current industrialized medicine. Last year I underwent a hiatal repair laparoscopic surgery. The best I can ascertain from the Medicare summary notice, which included everything administered the day of the procedure through an overnight stay in the hospital for observation with a release the next day, was the bill.
In addition, I experienced watching a son die at age 41 (Jeremy, the son who accompanied me to Mexico, leaving behind a wife and three small children, then ages 6, 4 and six months), not only from a rare lymphoma that kept him in a superior hospital in Chicago for more than five months but also from the side effects and complications of the aggressive cancer treatments. This all has given me additional perspective on medical approaches.
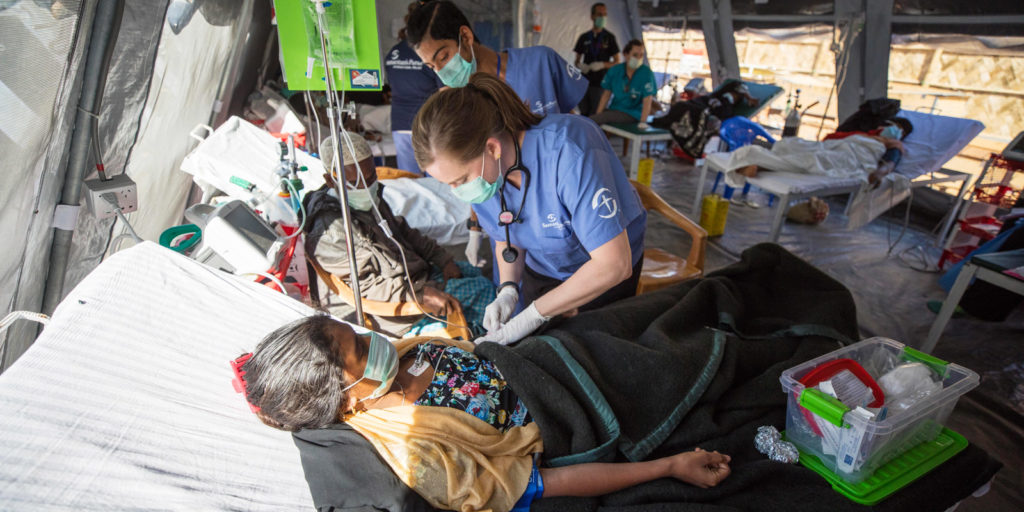
No Mosquitoes in the Room Now: A Quick Look at the Impact of Faith on Modern Medical Approaches
One of the most succinct summaries of the role of faith-based activity in relationship to ongoing health needs worldwide is a paper by Matthew Bersagel Braley, “The Christian Medical Commission and the World Health Organization.” In it, the author outlines the collaborative work done between the CMC and the WHO in the 1960s and 1970s. They both, concurrently and intentionally aided by the proximity of their headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, sought to address many of the deficiencies that were (and still are) growing apace modern Western medicine with its rapidly increasing dependence upon expensive diagnostic and curative technologies.
Braley’s abstract explains, after referencing the existence of two previous international consultations organized by the World Council of Churches out of which grew the Christian Medical Commission: “What followed was a theologically informed [italics added] shift from hospital-based tertiary care in cities, many in post-colonial settings, to primary care delivery in rural as well as urban communities.”
The early consultations, Tübingen I (in Germany) and Tübingen II, had developed a theology of health that eventually culminated in a mutual understanding. Looking as they were through the lens of health and defining health as the kind of flourishing that God intended for His human creation, they saw the mandate of the church as being that of working to restore (as much as is possible) the world to that original design. Wholeness then is a kind of health—an “at oneness” with God, with fellow humans, with our communities and with our environment. As believers work toward this goal, despite the fact it will never be ultimately achieved until Christ returns, they consequently become healers or health-bringers with an emphasis on flourishing.
Health was also redefined as the ideal that God desired for the people of the earth, one that will probably not be achieved completely, but will have periodic breakouts in time. Health was seen not simply as the “absence of disease” as defined traditionally by the medical establishment, but the presence of ecological health, harmony within the community, at oneness within the individual and in his or her relationships. It was a presence of peace and a lack of warfare; it was an insistence and concern that the neglected, the poor and the oppressed should even be given preferential treatment because of the systemic unfairness, lack of parity and often true evil exercised by the powerful over the powerless.

Personal Reflections
These theological comprehensions and conclusions have personal meaning to me, because I’ve seen firsthand the importance of working together to help others achieve this all-encompassing health. In 1967 we planted a church on the near west side of Chicago, across the expressway from what is now the Illinois Medical District. At that time, we knew it was one of the largest medical centers in the world; now it consists of 560 acres of medical research facilities, labs and a biotechnology business incubator, four major hospitals, two medical universities and more than 450 health care-related facilities. Needless to say, our small but rapidly growing congregation consisted of many medical grad students, nurses and doctors, and social workers.
There must have been something in the international waters, because totally unaware of the groundbreaking conversations going on among the professionals concerned with health impacts on the other side of the world, David Mains, my husband and the founding pastor of our church, discovered Christ’s major preaching theme was the Kingdom of God. Salvation, or being saved, was entry level to an understanding of that preeminent theme. If the predominance of this message was correct, then it totally shifted our thinking from an individualistic interpretation of faith lived out among private lives to a corporate identity framed through the mutual understanding of Scripture’s teaching of this breakthrough concept. Our salvation was worked out in dialogue around Scriptures and in community with other spiritual pilgrims.
There were places in the world, I discovered as I traveled in the role of journalist, where the people used the word “I” but really meant “we.” I began to understand the Epistles often addressed readers with the word “you.” This was not an individual personal pronoun; in most cases, it was a plural pronoun requiring group action, as in “you, the people of God.” David preached a sermon series titled The Christian, the Church and Society including Christ’s two-part summary message, “Unless you are converted and become like little children, you will by no means enter the kingdom of heaven.” The dialogue of those Christians, listening to David’s sermon in that place and that time in history, when a whole revolutionary resistance movement was rising in our culture—against the war in Vietnam and against injustice, racism, sexism and government corruption—forced upon us a theological conversation that just didn’t happen in other places.
In addition, David, in his 30s, became the head of the Greater Chicago Ministerial Association, and we learned to dialogue across the whole body of faith-based confessions. So, we understand how important it is when members of faith-based consultations here at home or far away across the world put aside their differences and in respect and with deep listening capabilities design outcomes that have the possibility to alter cultures and societies and whole nations for the good.

Conclusion: Our Part in World-Changing
Matthew Braley’s chapter, taken from the book Religion as a Social Determinant of Public Health, is filled with theological terminology such as epistemology and eschatology, but for the average layperson, what is most important is the Christian Medical Commission’s (CMC) understanding that God’s desire for humankind was that humans flourish in environments most optimal to health as defined not by the absence of disease but by a growing wholeness, and that the thrust of Christ’s ministry and preaching demonstrated the ways to achieve this, aptly summarized in His explanation that we are to love God and love our neighbor as ourselves. The CMC’s struggle to understand redemption as a growing wholeness eventually resulted in the “game-changing” 1978 Declaration of Alma-Ata, the conference out of which the Millennium Development Goals proceeded.
Everybody
is needed in order to fight diseases such as Ebola, HIV/AIDS or tuberculosis
All eight of those goals, delineated earlier in this article, are undergirded by and initiated from a theological understanding of the health emphasis, the redemptive purpose, the salvific meaning demonstrated by Christ and often emulated (though not often enough) by His followers. The MDGs are basically communal in the fact that they bring healing in the large sense of being at peace—or at home—with one’s self; with one’s family, friends and community; and with one’s place in the world. And they cannot be accomplished in a village or a nation or globally without the commensurate communal action of as many entities as possible, giving whatever they can to eradicate whatever suffering can be done away with through these human initiatives.
The participants at Tübingen I and II, the emergent Christian Medical Commission, and thousands of others of us who have, as the Jewish phrase states, worked at “repairing the world” for most of our lives would insist this is God’s work, in God’s way and with God’s help. Fortunately, as Bishop Tutu of South Africa said when he addressed the 2008 61st-annual meeting of the World Health Assembly, the World Health Organization’s governing body, “It is a godly coincidence … together WHO and WCC share a common mission to the world, protecting and restoring body, mind, and spirit.”
As Sharon Bieber responded: “Surely the relief and development organizations that are out there in the world can come to the same conclusion on this one thing—everybody is needed in order to fight diseases such as Ebola, HIV/AIDS or tuberculosis; every agency has strengths that will add to the synergy of the whole.”
So when we see groups like Gospel for Asia (GFA) working to hand out hundreds of thousands of mosquito nets to fight malarial infection, when we know tens of thousands of wells have been dug to provide clean water, and when we understand that the effectiveness of the message of Christ can often be measured by how many latrines have been built in a village or a city, we understand that this is what is necessary to help the participants in our world discover true, full health.

Who knows what consultations among desperate folk with common passions are forming even now that will salvage our world at some future critical juncture?
 Perhaps you would like to be part of that network of people determined to spread goodness (God-ness) throughout the world. First, begin by educating yourself. Read the book Half the Sky by Nicholas Kristof and his wife, Sheryl WuDunn, which includes a compendium of organizations seeking volunteers. The authors do not hide how impressed they are with conservative faith-based organizations doing work in the world. Another book to read is To Repair the World by Paul Farmer, a medical doctor many consider to be a modern-day hero.
Perhaps you would like to be part of that network of people determined to spread goodness (God-ness) throughout the world. First, begin by educating yourself. Read the book Half the Sky by Nicholas Kristof and his wife, Sheryl WuDunn, which includes a compendium of organizations seeking volunteers. The authors do not hide how impressed they are with conservative faith-based organizations doing work in the world. Another book to read is To Repair the World by Paul Farmer, a medical doctor many consider to be a modern-day hero.
“This is a bold read by a humble visionary. For those who care about humanity, this is a handbook for the heart,” reads a blurb on the back cover written by Byron Pitts, the chief national correspondent for CBS Evening News.
Then circle one of the volunteer efforts that seems to be calling your name. Become an activist. No need to travel overseas (although that is highly recommended). There is plenty of work to do at home, wherever home may be for you. Just don’t only think about doing something: Do it! (I’m going to look up volunteering for disaster-relief training with The Salvation Army—or the American Red Cross—and I’m 76 years of age!)
At the end of the parable of the Good Samaritan, Jesus says to the young lawyer, “Go and do likewise.” No, there’s no danger pay for the faith-based health worker. I don’t know of any who have become wealthy. Most of them belong to the league of the nameless. For these, fame is not a motivator either; it generally gets in the way of doing the job.
But mercy? Compassion? Daring to go where others dare not go? Becoming more and more like Jesus? Yep, these are where most of those I know find deep satisfaction. A remarkable man once said, “Go and do likewise.” And they do.
Is that a mosquito I hear buzzing above my ear?
It only takes one mosquito bite to raise a welt.
It only takes one mosquito to kill a child.
It will take a multitude of innovators (believers or nonbelievers) to fight for the Kingdom to “come on earth as it is in heaven.”
To read more news on Malaria on MissionsBox News, go here.
This Special Report originally appeared on gfa.org.
Learn more about how Mosquito Nets offer protection for families, saving them from the sickening agony or death from malaria.
For more information about this, click here.





